
The Committee for Private Education (CPE) was appointed by SkillsFuture Singapore (SSG) Board in October 2016 to carry out its functions and powers relating to private education under the Private Education Act. CPE has implemented a mandatory registration tier to enhance the private education standards and a voluntary quality assurance framework known as EduTrust Certification Scheme, for schools who wish to recruit students from foreign countries.
Under the EduTrust Certification scheme, private education institutes must adopt the Fee Protection Scheme (FPS) with CPE-appointed service providers and provide medical insurance coverage for hospitalization and related medical treatment for the entire course duration.
EduTrust Certification Scheme is a voluntary scheme that helps to distinguish players in Singapore’s private education industry.
Although it is a voluntary scheme, it is a pre-requisites for private education institutions who wishes to enrol international students and in order to qualify for the issue of Student’s Passes, as stipulated by the Immigration and Checkpoints Authority (ICA).
DIMENSIONS International College is proud to have attained the 4-Year EduTrust Certification awarded by Committee for Private Education (CPE).
 Click here for Private Education Institution Registration and EduTrust Certificate.
Click here for Private Education Institution Registration and EduTrust Certificate.
For more information, please visit CPE’s website at https://www.ssg.gov.sg/cpe/pei.html
| CERTIFICATION | CHARACTERISTICS |
EduTrust Star  |
EduTrust Star (750 points and above)
Award is given to a PEIs for attaining a commendable level of performance in managing their institutions and providing an outstanding quality of education and welfare for their students. This mark is a symbol of recognition for outstanding achievement. The EduTrust Star has a validity of up to four years. |
EduTrust  |
EduTrust (600 to 749 points)
Award is given to PEIs for sustaining an excellent level of performance in managing their institutions and providing high quality education standards and welfare for their students. The EduTrust has a validity of up to four years. |
EduTrust Provisional  |
EduTrust Provisional (500 to 599 points)
Award is given to PEIs that have attained a minimum level of performance in key areas of administration and provision of educational services. The EduTrust Provisional has a validity of up to one year. In accepting the award, the PEI acknowledges the need for improvements to meet the level of performance expected of the four-year EduTrust award in its existing management practices and service provisions, and strives to achieve this. |
「台湾財團法人高等教育評鑑中心基金會,简称HEEACT」係於 2005 年 12 月正式成立,其主要任務為負責進行高等教育之評鑑與考核,並包括研發評鑑指標、培養評鑑人才、開發更好的評鑑機制,同時與國外重要評鑑機構進行交流,確保台灣大專院校提供高品質的教育。本基金會係由教育部與大學共同捐助而成立,願景是要秉持「公正專業、邁向卓越」的精神,進行優良公正的評比與評鑑。
Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA);Strengthening and Empowering The Quality of Malaysian Higher Education

Malaysia has experienced enormous growth in higher education over the last two decades, especially in the growth of public and private higher education institutions. This phenomenon has in turn increased the number of programmes offered in Malaysia, from certificate up to doctorate level.
Previously, matters pertaining the quality of education were managed internally by the public universities through its Internal Quality Assurance (IQA) system. This was because of the small number of higher education institutions, which were mainly public institutions. Presently, the function of the External Quality Assurance (EQA) system has become as important as the IQA. The Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA) is now the main quality assurance and accrediting body as stated in the MQA Act 2007 and has the responsibility of assuring the quality of both public and private higher education programmes in Malaysia.
Besides the quality of higher education institutions, quality assurance practices have also evolved tremendously in recent years. The Malaysia Qualifications Framework (MQF) was established to illustrate all levels of higher education in Malaysia, and serve as a national reference point for all Malaysian qualifications.
Without compromising the quality of programme accreditation practices, Malaysia has also started to empower the responsibilities of quality assurance to higher education institutions by introducing a self-accrediting process. This gives certain institutions the authority to accredit its own programmes, with regular monitoring by MQA. It is one of the many efforts of the ministry to continuously strengthen the quality of higher education in Malaysia
The changing trends in quality assurance show that quality assurance is an ongoing process which involves the undertaking of several. MQA is committed to continuously reviewing its quality assurance practices to ensure their relevancy, reliability, adaptability and effectiveness to address the ever changing environment in which higher education operates.
Establishment
On 1 November 2007, the Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA) was established when the Malaysian Qualifications Agency Act 2007 came in force. The transition from the National Accreditation Board (or called Lembaga Akreditasi Negara, LAN in Malay) to MQA symbolised the maturing of quality assurance in Malaysian higher education. The international good practices of quality assurance agencies were also incorporated into the organisation structure of MQA.
With the vision to become a credible and internationally recognised higher education quality assurance body and the mission to inspire the confidence of its stakeholders through best practices, MQA is set to chart new boundaries in higher education quality assurance. As such, quality assurance in Malaysian higher education is benchmarked beyond the conventional definition of quality assurance to specifically and consciously include the idea of continuous quality improvement
Functions
As the main quality assurance and accrediting body in Malaysia, MQA plays a vital role in assuring the quality of higher education in both public and private institutions. The functions of MQA include:
In addition, MQA has also widened its function internationally, in which MQA also evaluates foreign qualifications and assesses its comparability in relation to MQF.
Organisation
MQA consists of three entities: the Council, the Committees and the Agency. This structure was established with the objective of ensuring the inter-agencies involvement, impartiality and transparency in the Agency’s quality judgments as well as efficiency in its daily operations.
The Council

MQA is headed by a Council. The Council is chaired by a non-executive Chairman, with 17 members from related ministries largely responsible for human resource development, professional bodies, industry, members of Parliament, public and private institutions of higher learning and experts with vast experience in higher education. They form the principal stakeholders in the higher education sector and a reflection of the strong commitment to collaborate with them.
The main roles of the Council are to approve plans and policies for the management of the Agency; to approve amendments and updates of the MQF; to approve policies and guidelines relating to audit processes and the accreditation of programmes, qualifications and higher education providers; to receive and monitor reports, returns, statements and any other information relating to accreditation, institutional audit and evaluation; and to continuously guide the Agency in its function as a quality assurance body and do all things reasonably necessary for the performance of its functions under the Act.
The Agency
The Agency is headed by the Chief Executive Officer with the assistance of three Deputy Chief Executive Officers and run by a staff of 350. The quality assurance undertakings of the Agency are supported by about 1,300 assessors and auditors.
The committees
Major committees are the Accreditation Committee, the Institutional Audit Committee, the Equivalency Committee and the Standard Committee. Two Accreditation Committees cover the major areas of studies, i.e. the sciences and the arts. The functions of the Accreditation Committees are to evaluate and analyse accreditation reports; to make decisions on a higher education provider’s (HEP’s) application for provisional or full accreditation of programmes and qualifications; and to grant, deny, maintain or revoke provisional accreditation or full accreditation of programmes and qualifications
The Institutional Audit Committee is responsible for evaluating and making recommendations on institutional audit reports; making the final recommendation on the awarding, or otherwise, of institutional self-accreditation status; and making recommendations for the maintenance, suspension or revocation of self-accreditation status.
The key function of the Equivalency Committee is to make decisions on the equivalency of qualifications for their placement in the level of qualifications in the Malaysian Qualifications Framework (MQF).
The main functions of the Standards Committee are to develop and review the guidelines, standards and criteria for programme accreditation and institutional audit; to develop and review standards for specific disciplines; and to develop and review guides to good practices
Accreditation of Professional Programmes
Peculiar to the Malaysian scenario, under the MQA Act 2007, programmes of higher education institutions that lead to professional qualifications require accreditation to be done by or in close collaboration with the respective professional bodies. These are professional bodies established under various Acts of Parliament to regulate the profession through the licensing of practitioners. The relation with MQA is operationalised through a joint technical committee. These programmes include medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, architecture, engineering and several others. Generally, accreditation for the programme also means recognition from the professional bodies.
The Quality Assurance System
Best practices for quality assurance calls for clearly defined, transparent and fair criteria and standards that serve as references for evaluations and reports of programmes offered by higher education providers. In designing and delivering their programmes, higher education providers are guided by the Malaysian Qualifications Framework (MQF); the Codes of Practice for Programme Accreditation and Institutional Audit; Programme Discipline Standards; and Guidelines to Good Practices. Quality assurance in Malaysia begins with MQF. With full enforcement of this Act, it is intended that all higher education programmes and qualifications must be in compliance with MQF.
The Malaysian Qualifications Framework (MQF)
MQF is Malaysia’s declaration about its qualifications and their quality in relation to its education system.
The process of developing the framework began as early as 2002 under the auspices of the National Accreditation Board (LAN) with a series of intensive national consultations before being approved by the National Higher Education Council and the Cabinet. The framework was launched in 2007 with the establishment of the MQA, which was given the responsibility as the guardian of MQF.
MQF is an instrument that develops and classifies qualifications based on a set of criteria that are approved nationally and benchmarked against international best practices, and which clarifies the earned academic levels, learning outcomes of study areas and credit system based on student academic load. These criteria are accepted and used for all qualifications awarded by recognised higher education providers. Hence, MQF integrates with and links all national qualifications.
MQF also provides educational pathways through which it links qualifications systematically. These pathways will enable the individual to progress through credit transfers an d accreditation of prior experiential learning, in the context of lifelong learning.
These Codes of Practice provide guidelines of general requirements in the following areas:
Curriculum design and delivery;
In general, MQA quality assures programmes through two distinct processes, i.e. Provisional Accreditation and Full Accreditation. Provisional Accreditation is a candidacy assessment to determine the strength of curriculum to be offered and the readiness of its delivery support system before it is being offered to the public. Provisional Accreditation is granted with a validity period to a particular programme. The programme is required to undergo a Full Accreditation exercise prior to the expiry of the validity period.
In contrast, Full Accreditation is an assessment exercise at the end of the first cycle of a programme. This exercise is meant to verify that the programme is in compliance with MQF as well as to ascertain the appropriateness and adequacy of the programme’s educational arrangement as set by the code of practice.
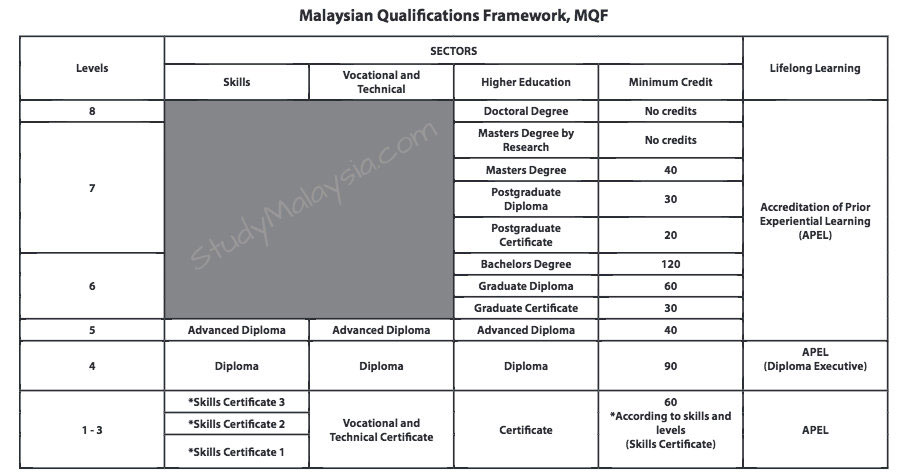
The Eight Levels of MQF Qualifications
MQF has eight levels of qualifications in three national higher education sectors and is supported by lifelong education pathways (see Table 1). The sectors are (a) Skills, (b) Vocational and Technical and (c) Higher Education.
Levels 1 to 3 are Skills Certificates awarded by the Skills Sectors. Higher Education and Vocational and Technical Certificates are at level 3. Meanwhile, Diploma and Advanced Diploma are at Levels 4 and 5. Bachelor’s Degree is at Level 6, Master’s Degree at Level 7 and Doctoral Degree at Level 8.
The levels are differentiated by learning outcomes, credit hours and student learning time.
Lifelong education pathways cut across all levels of qualifications through accreditation of prior experiential learning.
The Learning Outcomes
Student achievements are measured by learning outcomes. These learning outcomes distinguish the varying competencies as to what a student will be able to do at the end of a period of study. Learning outcomes are based on eight domains:
Practical skill;
Learning outcomes are linked to the credit system which gives value to the entire student learning time and are not based on the contact hours between lecturers and students.
MQA has also developed the Codes of Practice for Programme Accreditation (COPPA) and the Codes of Practice for Institutional Audit (COPIA). These Codes of Practice are benchmarked against international good practices and nationally accepted by stakeholders through various consultations.
Self Accreditation
The MQA Act 2007 also provides for the conferment of a self accrediting status to mature higher education institutions that have well established internal quality assurance mechanisms. To be so conferred, the higher education institution needs to undergo an institutional audit, and if successful, all qualifications it offers will be automatically registered in MQR.
The processes above are further supported by continuous monitoring to ensure the programmes offered by the institutions are always quality assured.